Welcome to the Native Gardens at The Nature Place
The Nature Place is surrounded by eight native gardens containing a multitude of native species, habitats, and educational opportunities. While the gardens are maintained by the Master Gardeners and the Master Naturalist, they fit right into the existing ecosystem. Not only are these gardens beautiful, but they also demonstrate the healthy codependency between flora and fauna. Keep reading to learn more about these impressive gardens and what you can do to support native plants.

Map of the Gardens
Garden Map
Click on any garden name on the map to view the typical plants found in that garden. You can scroll through the garden images to view them all.
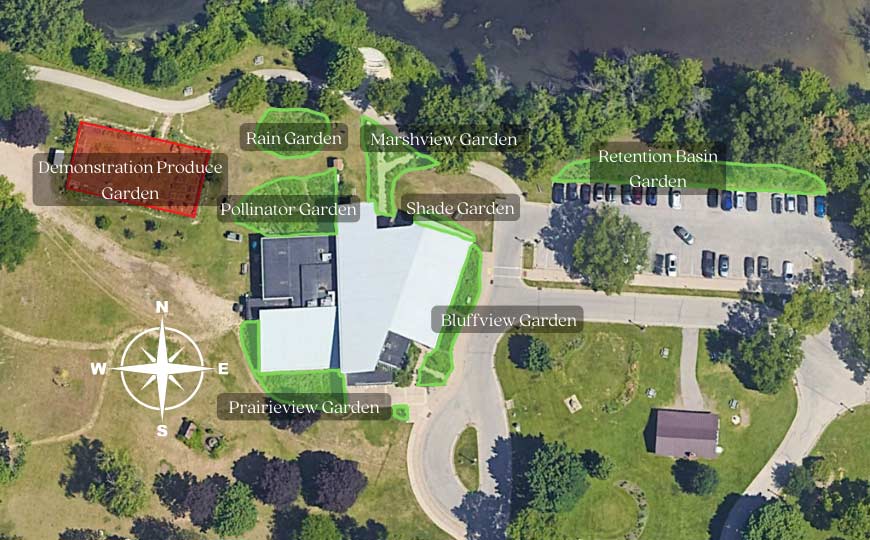
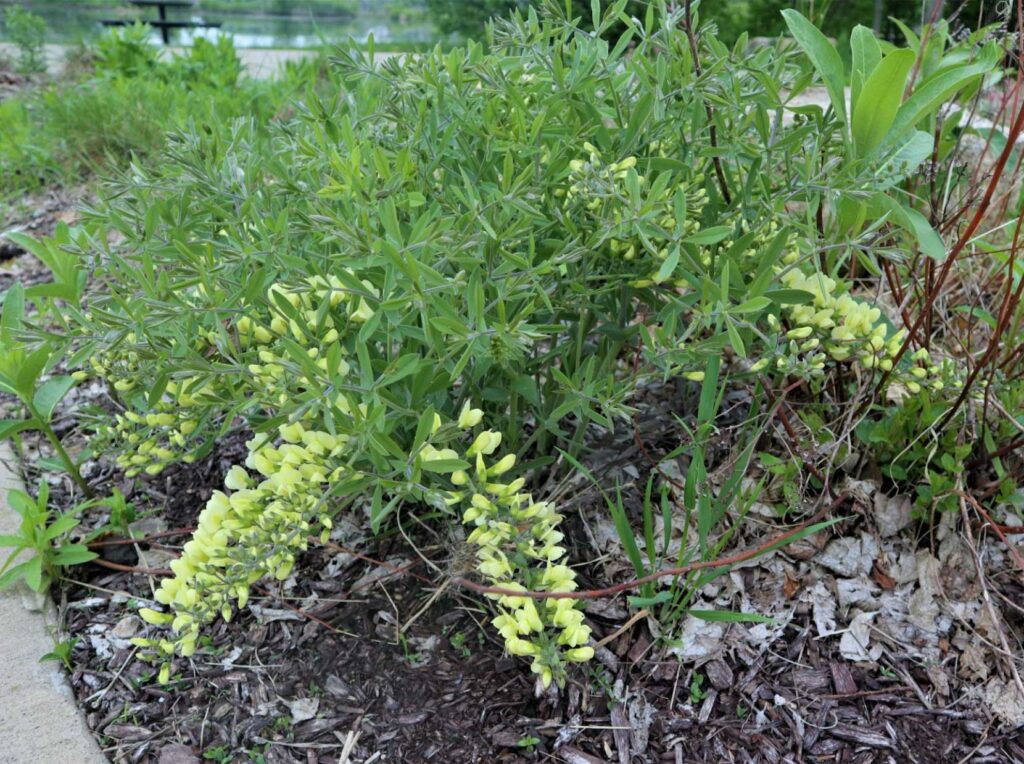
Rain Garden
Bluffview Garden
Prairieview Garden
Pollinator Garden
Retention Basin Garden
Shade Garden
Marshview Garden
Volunteer
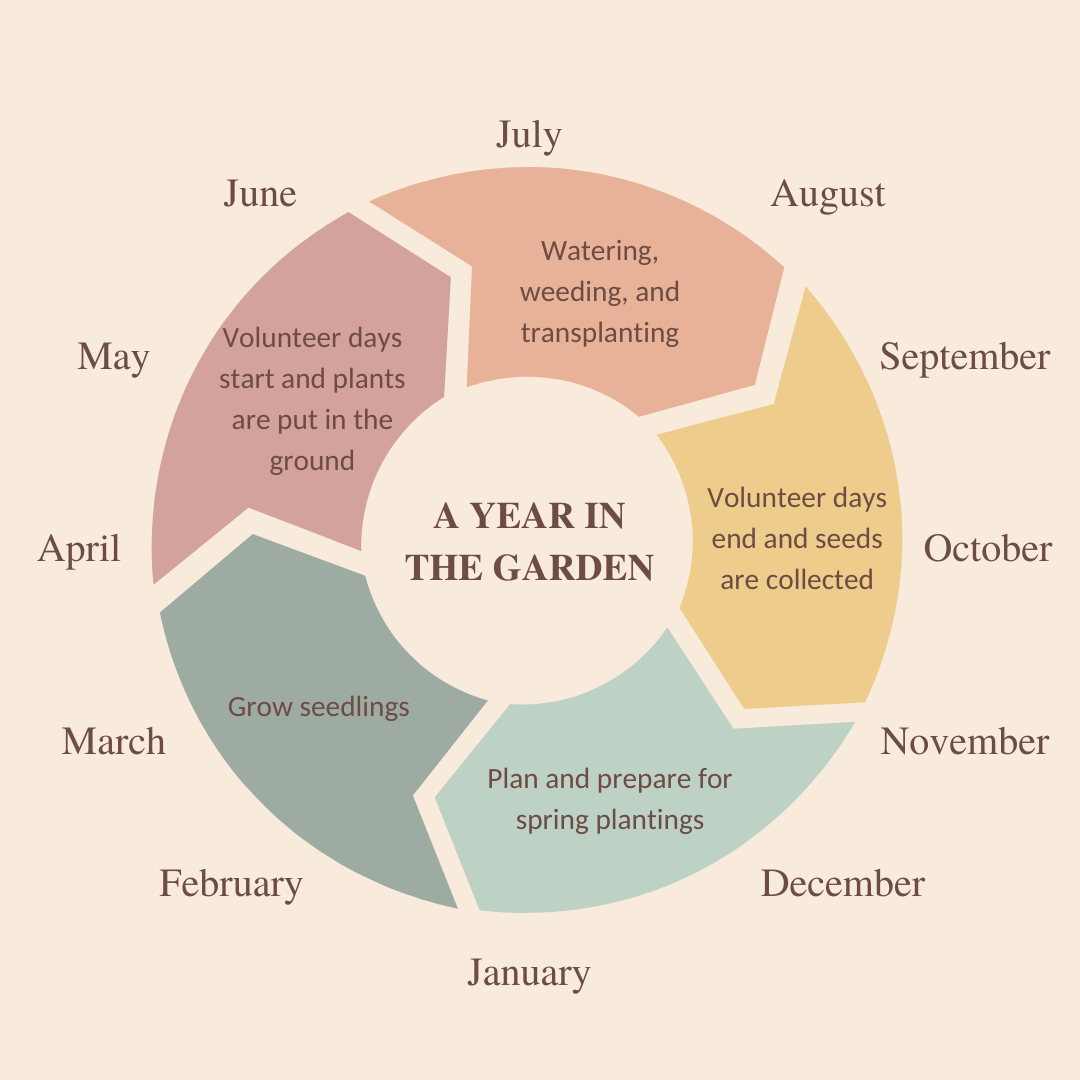
If you’re ready to get your hands dirty, we are always looking for volunteers!
Volunteers meet every Thursday from 9:00 - 12:00 May-October. However, if Thursdays don’t work for you, send an email to set up an alternative volunteer time.
Volunteering in the native gardens will include tasks such as:
- Planting new forbs, grasses, and sedges
- Removing weeds and non-native plants
- Transplanting seedlings to other gardens or raised beds
- Trimming plants to prevent tall or floppy growth
- Watering new plants
- Having fun!

What are Native Plants?
Definition:
A plant that has lived and developed in a particular region for over hundreds or thousands of years.
Native plants...
The Value of Native Gardens
Native gardens hold immeasurable value to their communities. To name a few, they supply food and habitat to native wildlife, are easier to maintain, encourage a deeper understanding of our relationship with the land, and are magnificent to observe.
Support Biodiversity and Crucial Wildlife
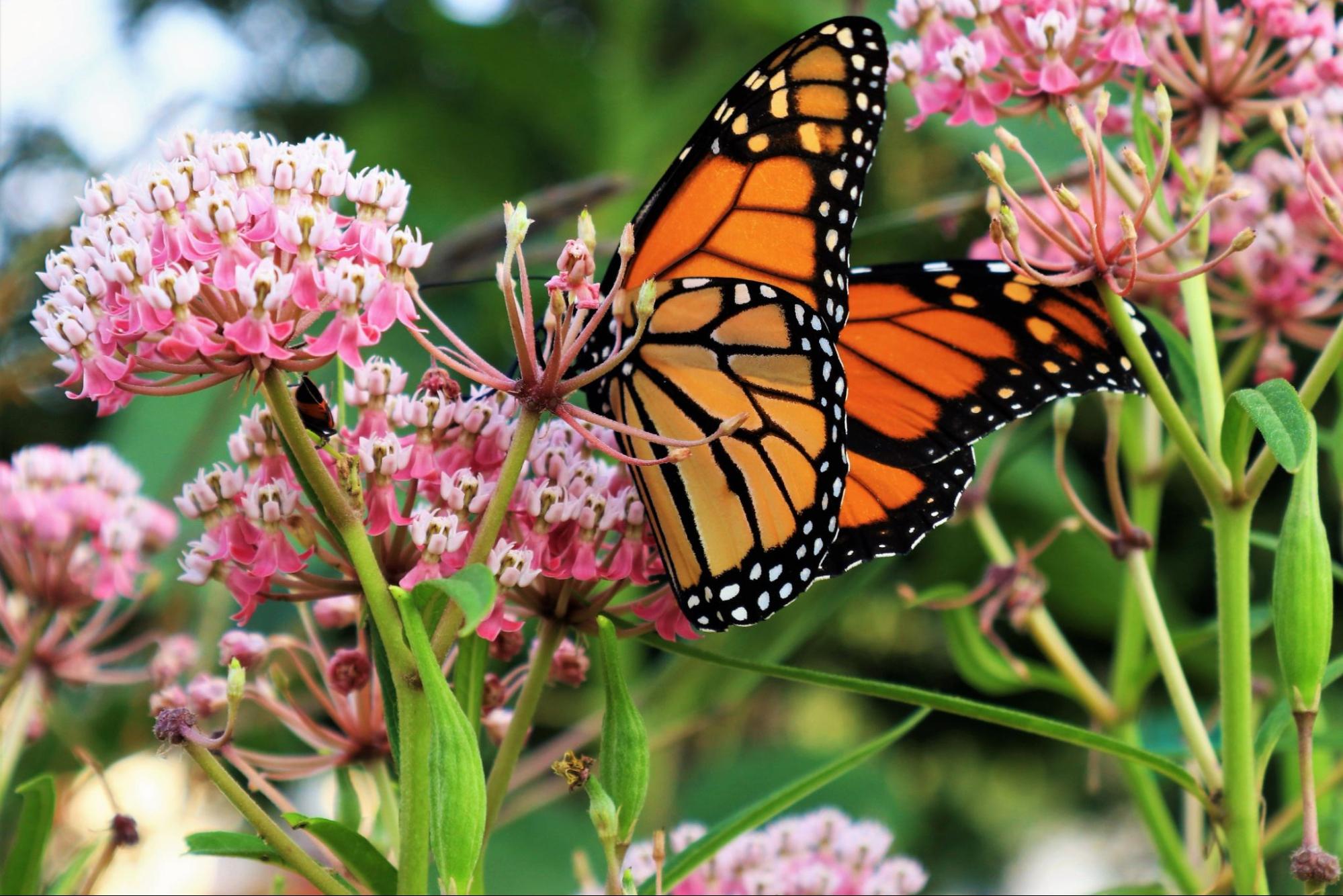
One of the biggest benefits of native gardens is the support they offer to native insects and biodiversity. Many of the plant species that we use for food or for decoration depend on a wide range of insects.
Some of the most crucial native insects include decomposers (who decompose organic material), pollinators (who assist with plant reproduction), and natural predators (who help control population levels). In addition to supporting human food systems, these insects also help maintain the food systems that support most other wildlife.
In short, native insects play a vital role in maintaining the world as we know it. However, these populations are declining due to competition with non-native insects and human practices of land development and pesticide use. Native gardens provide food and habitat for these species, helping them continue their essential work of maintaining ecosystem biodiversity.


Easier to Maintain
Compared to the typical manicured lawn, native landscaping requires less maintenance, less dependence on fossil fuels, less water, and practically no pesticide or fertilizer use.
Unlike common lawn practice, native landscapes do not need to be mowed. As most lawn mowers run on gasoline, this helps to reduce our use of fossil fuel energy.
Also, being that native plant species have co-adapted in their natural region, they have grown more resistant to challenges such as weather changes and weeds. They have a higher endurance to drought, as their deep root systems increase the soil’s water storage capacity. In turn, these root systems help reduce runoff, flooding, and soil erosion.
Lastly, pesticides and fertilizers often contain chemicals that, when introduced to the water systems via runoff, disrupt the natural ecosystem and damage water quality. Being native species are more resistant to things like weeds and insects, they do not require the use of pesticides or fertilizers the way non-native plants do. With all that being said, native gardens still need our love and attention in order to truly thrive!
Foster Relationships with the Land
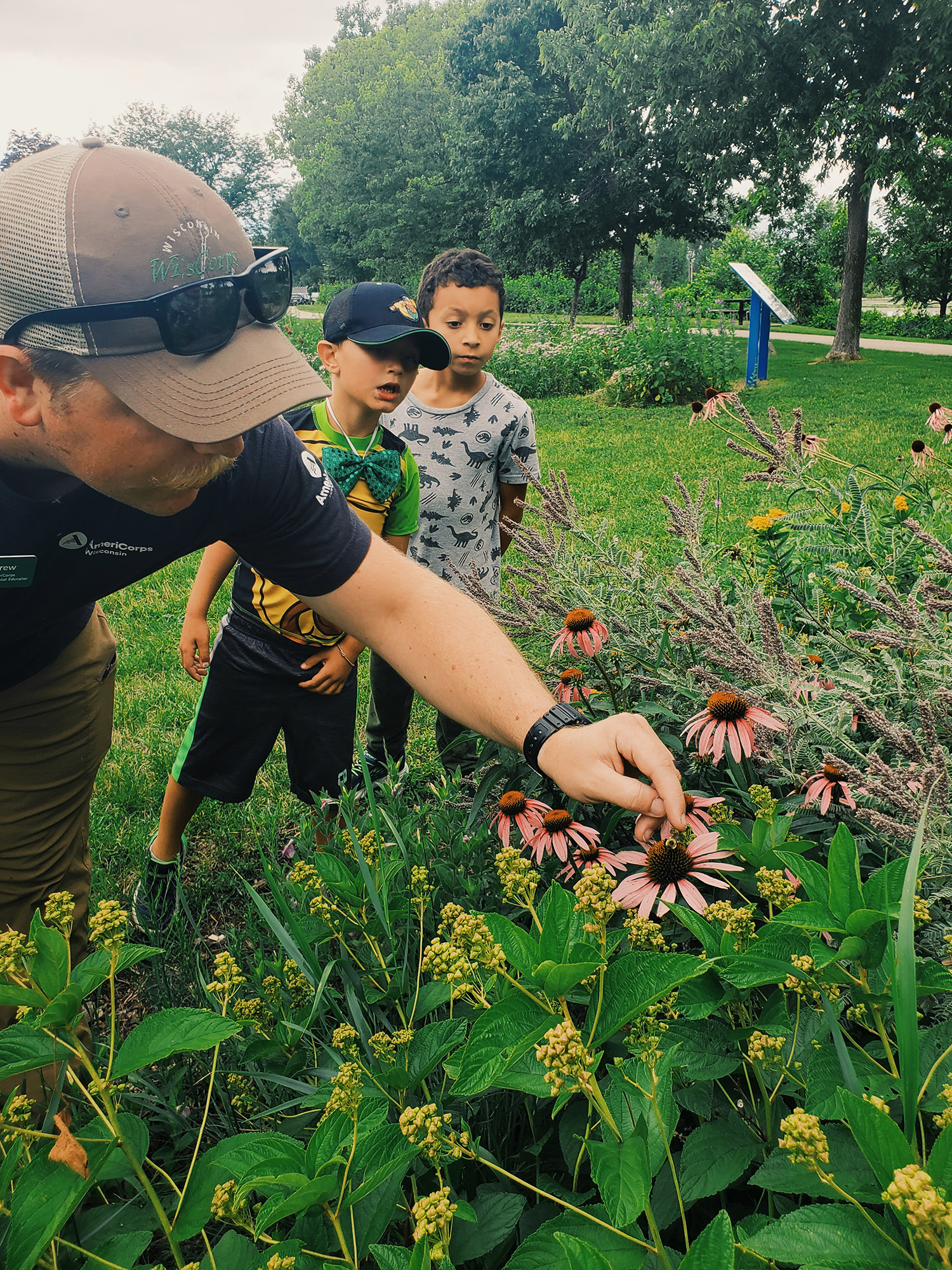
While human manipulation of the natural environment has been a consistent threat to native plants and animals, implementing native gardens is one way we can reestablish our relationship with this land. When we plant native gardens, we are able to observe up close the natural ecosystem we have inserted ourselves into. Whether you’re watching the birds, bees, butterflies, critters, or the thriving plants, you’re able to observe the fascinating roles these native species play.
Native gardens can provide us with educational insights, opportunities for recreation and relaxation, a chance to reflect on the natural world around us, and a deeper understanding of our role in that world.

Did you know?
Native oak trees support more than 500 species of caterpillars where non-native species, such as Ginkgos, host only 5 species (Narango 2020).
More than 90% of native butterfly and moth larvae are specialists, meaning they only feed on specific native plants and therefore cannot feed on non-native plants (Burghardt 2010).
The Origins of the Gardens
The Nature Place has had a long journey to get to what it is today. Before WisCorps settled in as its current host, the center was home to the Myrick Hixon Eco-Park and then the Myrick Park Center. Since WisCorps has moved in, eight native gardens have been planted through the help of the Bluff County Master Gardeners Association and in cooperation and assistance with the City of La Crosse. The master gardeners and other volunteers have planned and maintained each garden with care, creating a local treasure that is here to stay.
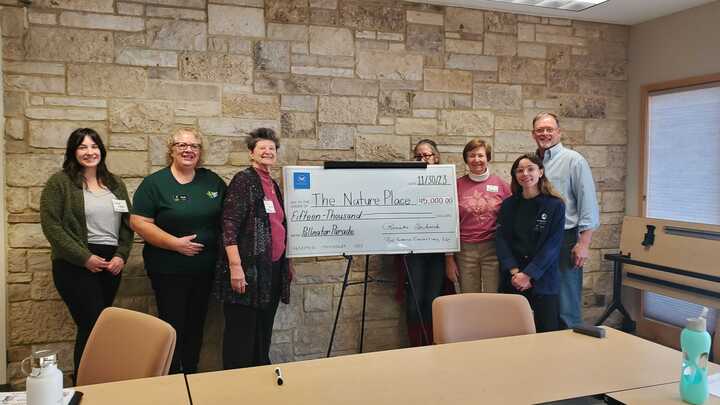




Pollinator parade children's book
The book, Pollinator Parade, began as a collaboration between Strive2Thrive Coulee Region, The Nature Place, and local author Nick Nichols, with editing by Rachel MacFarland and technical support from UW-La Crosse and Viterbo University Biology Departments.
Pollinator Parade is a fictional narrative that follows two siblings as they visit their grandparents’ pollinator garden, learning about the wild array of interesting creatures that “parade” through the plants and keep our ecosystem alive. Pollinator Parade includes scientifically accurate illustrations by Pete Hodapp, an insect index, and other resources for all ages to get involved in creating critical natural spaces for pollinators. It also connects readers to Operation Pollination, a partnership project aiming to restore pollinator habitats.
Books will be freely distributed to schools in the local area after the anticipated release date of April 2024. The Nature Place will utilize the book in programming and also have it available on-site for purchase. Profit sales will go back to support The Nature Place and Operation Pollination.
The Nature Place AmeriCorps members, Abby Friell and Gabrielle Arnold, have served as project managers, under the mentorship of Stephanie Hanna, Community Program Manager. Funding for this project was generously donated by Roz Schnick Consulting LLC and Strive2Thrive.
Testimonials
“I enjoy spending time at Myrick because I learn so much, feel challenged, and also leave thinking I’ve contributed some small part to creating a habitat beneficial to plants and animals. Hopefully it also is attractive for the public to enjoy. I learn about diverse native plants and the wildlife they attract through work and observation, from the other volunteers, and from research. Helping to create and maintain the Myrick Native Gardens is a labor of love. I am always mindful that it serves as an example of using plants native to our geographic area in a garden type setting.”
– Elizabeth Kruck, Master Gardener and Volunteer
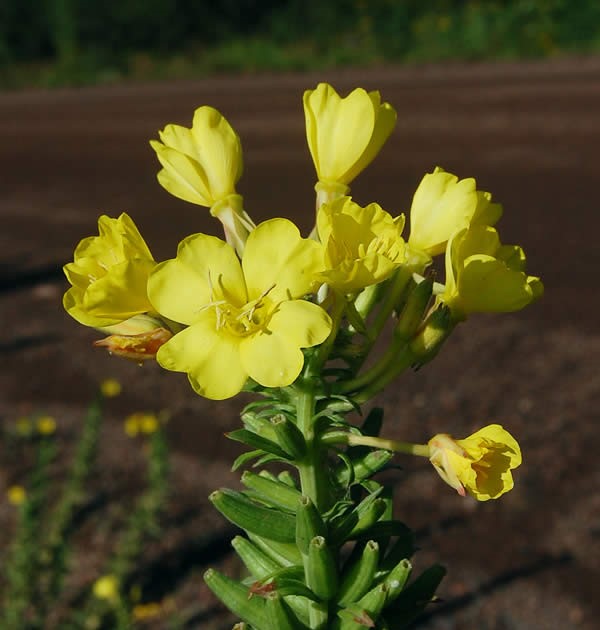
Native Plant of the Week
Evening Primrose (Oenothera biennis)
How to Identify:
-
2-6 feet tall
-
Lance shaped leaves that grow up to 8 inches long
-
Rough feeling, hairless leaves
- Many flowers bloom at once from a terminal spike
- Flowers are yellow with four heart shaped petals
Habitat: Native throughout the majority of the Eastern United States, Evening Primrose is mainly found in fields, along roadsides, forest edges or near steams
Bloom Season: July-October
Did You Know? Evening primrose opens its flowers at night, and closes them in the heat of the day!
Come find me in the Pollinator Garden!

Your feedback helps us continually improve
Additional Resources
Wild Ones Webinars
Doug Tallamy:
Watch: Nature’s Best Hope
Watch: Oaks
Heather Holm:
Watch: Bumble Bees
Watch: Wasps
Ken Williams:
Watch: 10 tips for New Gardeners
The Nature Place Resources
Purchasing Native Plants
Driftless Area Natives
Prairie Moon Nursery
Prairie Nursery
Why Native Plants Matter
Read: Audubon
Read: Prairie Nursery
Wild Ones Readings
Read: Installing a Native Garden
Read: Benefits of Native Plants



































































































































































































